Corporate information security, part 1 — Why can’t I invest in information security like I can in green companies?
Protection and testing
Corporate information security, part 4 — Protection and testing
When the threats have been identified, the firewalls are up and information security is being monitored by SOC, doubts often start creeping in. Is the company really protected against all information security threats? How can you tell whether your safeguards and coverage are good enough?
This corporate information security blog delves into comprehensive safeguards and their testing.
Prevention, detection or correction?
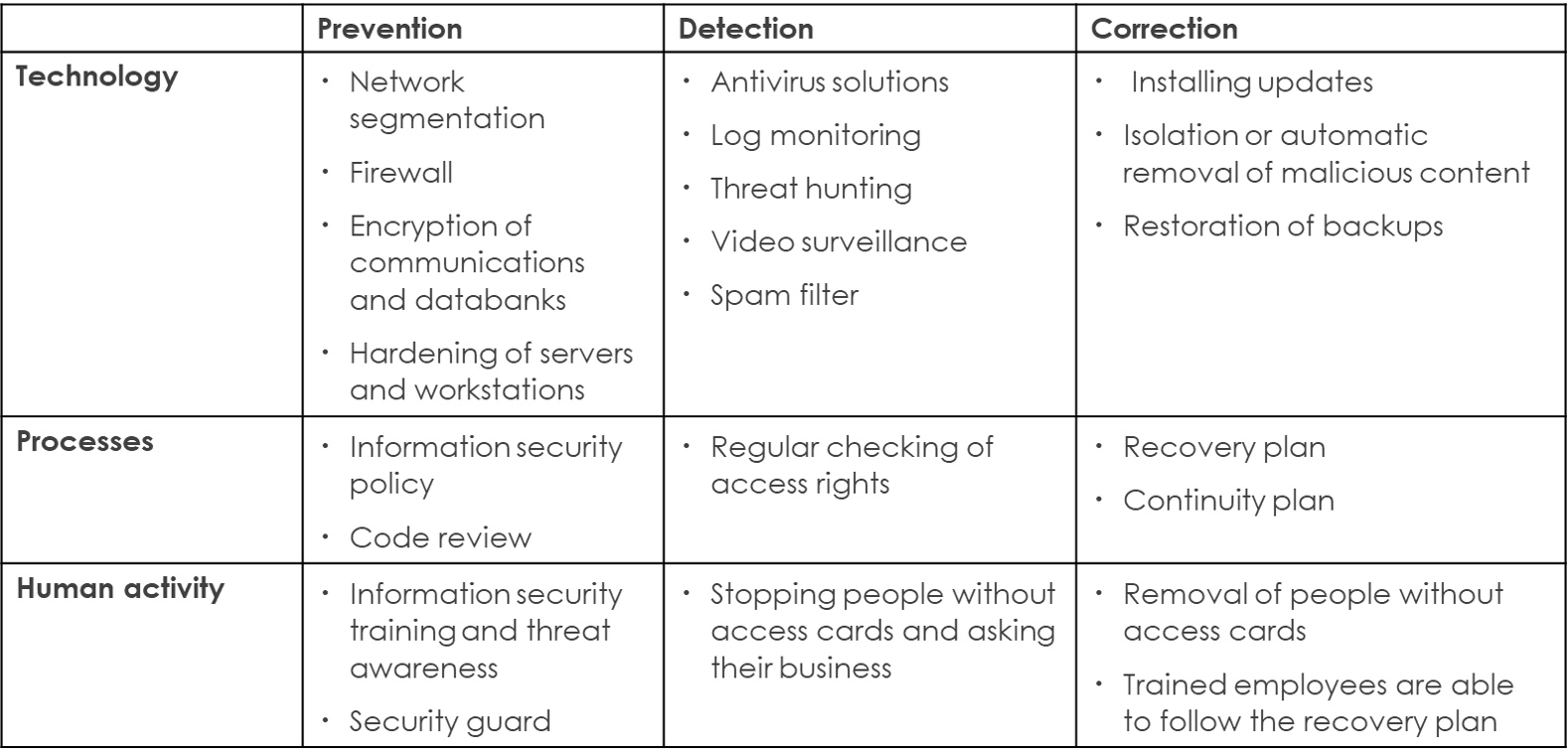
Safeguards against information security threats can be divided into three main categories:
- Prevention
- Detection
- Correction
Preventing every attack with 100% certainty is not realistic, zero-day vulnerabilities can always occur or a clever social engineer can fool an employee into letting the cybercriminals into the network. For this reason, you should never neglect detective and corrective measures in your information security toolkit.
You should also choose your safeguards according to your company’s threats and risks (we’ve covered their identification and assessment in previous posts). However, you don’t need to take your information security overboard, for example encrypting your information may not be a practical security measure if the principal threat is unauthorized editing of your data. In such cases, you might want to look at integrity checks or digital signatures instead.
Preventive technical safeguards include network segmentation, firewalls, encryption of communications and storage media, and hardening of workstations and servers. Preventive measures also include processes, such as information security policies and code reviews. Influencing the way people act, for example by organizing regular information security training is a highly effective preventive safeguard.
Detection measures include antivirus software, log monitoring, spam filtering, intrusion detection systems (IDS) and threat hunting. When an employee spots a person without an access card and asks what their business is, that’s a preventive measure too.
With successful detection, you can initiate corrective measures as early as possible, letting you mitigate the damage caused by the attack or maybe even prevent it altogether. Corrective safeguards include the automated isolation or deletion of malware, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), installing information security patches, continuity, and recovery plans.
As you may have gathered from the list above, safeguards can involve:
- Technology
- Processes
- Human activity
A layered defense combines several types of safeguards.
Examples of safeguards against information security threats.
Don’t forget to test your processes and how your people react to incidents
As safeguards cover technology, processes and human behavior, so should your testing. You have several options available:
Technical Security Testing
Technical security testing measures the functionality of your services, applications or IT systems technical security safeguards and identifies potential vulnerabilities in system components or operational logic. A technical information security audit looks at one or more of the following areas:
- Client applications, such as web interfaces and mobile apps
- Server-side applications and databases
- Server platforms
- Data communications
- Management interfaces and connections to other systems
- Data processing environments (e.g. cloud platform) and architectures.
A typical technical audit evaluates the system against predefined standards or information security criteria, such as the Application Security Verification Standard (ASVS), Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS), OWASP Top 10, or other best practices and hardening guidelines.
Red Teaming
A red team attack test identifies how well your people, technical safeguards and processes work together when facing a targeted attack. A red teaming exercise can include using open sources to assess the data available on your company. I can also identify your company’s surface attack, test penetration on the information system, test facility access and can find out how your employees react to phishing messages or social engineering. You can read more about red teaming on our blog.
Detection and Monitoring Capabilities Testing
Technical security testing, often solely focuses on preventive safeguards. You should also test how well your log monitoring or threat detection and response systems detect simulated attacks. This paints a picture of your detection and monitoring capabilities and possible blind spots for the eventuality of a real attack. In addition, the SOC and other experts processing your event logs receive valuable training in incident management and response.
Information Security Training
Recruiting a capable information security manager and appointing a Data Privacy Officer is not going to guarantee your information security in today’s environment. Most corporate information security threats target employees in the guise of phishing messages or social engineers approaching your personnel on LinkedIn for example. That’s why it’s worthwhile to train your staff and share information on the latest cyber threats via your company’s internal communications channels. However, before you do this, you should take a moment to identify the fraud attempts or other information security threats your employees could face in light of your company’s tools, line of business and employee duties. Instead of just painting the proverbial devil on the wall, it’s important to inform your staff of why the threats are significant and what they can do to mitigate them.
Corporate information security, part 4 — Protection and testing
Cybersecurity Exercises
It can also be useful to test how well your corrective measures and processes, such as recovery and continuity plans or the restoration of backups, work in a real-life situation. Communication, information sharing, and logging measures taken in the event log often also require a bit of practice.
A cybersecurity exercise can be anything from a short workshop to review your process phases to a live exercise to practice decision-making and communications during a simulated information security incident, such as a ransomware attack or a multi-day technical drill in which you defend yourself against cyberattacks implemented by the other players. See our blog and service pages for more examples of cybersecurity exercises.
Protecting Yourself and Testing your Defenses is a Continuous Exercise
Information security threats evolve with time and new vulnerabilities are discovered in existing products. You should therefore test the security of your information systems and functionality of your safeguards on a regular basis. This can also prevent unnecessary costs, such as paying for technology with negligible security benefits.
Practice also makes perfect, so training and cybersecurity exercises should be a regular thing for your personnel.
This blog post is part of a series on information security and awareness. The previous part dealt with risks and responsibilities. The next instalment will discuss how much startups should pay for information security.
